Question 2
Directions: SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. REMEMBER THAT PROGRAM SEGMENTS ARE TO BE WRITTEN IN JAVA.
Notes:
Assume that the classes listed in the Java Quick Reference have been imported where appropriate.
Unless otherwise noted in the question, assume that parameters in method calls are not null and that methods are called only when their preconditions are satisfied.
In writing solutions for each question, you may use any of the accessible methods that are listed in classes defined in that question. Writing significant amounts of code that can be replaced by a call to one of these methods will not receive full credit.
Consider a guessing game in which a player tries to guess a hidden word. The hidden word contains only capital letters and has a length known to the player. A guess contains only capital letters and has the same length as the hidden word.
After a guess is made, the player is given a hint that is based on a comparison between the hidden word and the guess. Each position in the hint contains a character that corresponds to the letter in the same position in the guess. The following rules determine the characters that appear in the hint.
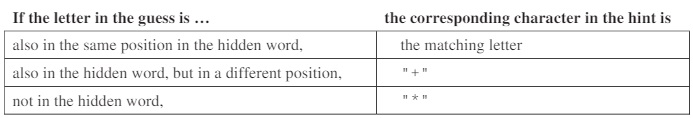
The HiddenWord class will be used to represent the hidden word in the game. The hidden word is passed to the constructor. The class contains a method, getHint, that takes a guess and produces a hint.
For example, suppose the variable puzzle is declared as follows.
HiddenWord puzzle = new HiddenWord(“HARPS”);
The following table shows several guesses and the hints that would be produced.

Write the complete HiddenWord class, including any necessary instance variables, its constructor, and the method, getHint, described above. You may assume that the length of the guess is the same as the length of the hidden word.
public class HiddenWord {
private String word;
// Constructor to initialize the hidden word
public HiddenWord(String hWord) {
word = hWord;
}
// Method to generate a hint based on the guess
public String getHint(String guess) {
String hint = "";
// Ensure the guess length does not exceed the hidden word length
int maxLength = Math.min(guess.length(), word.length());
// Loop through each character in the guess
for (int i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) {
// Check if the character in the guess matches the character in the same position in the hidden word
if (guess.substring(i, i + 1).equals(word.substring(i, i + 1))) {
hint += guess.substring(i, i + 1); // If match, append the character to hint
} else if (word.indexOf(guess.substring(i, i + 1)) != -1) {
hint += "+"; // If the character exists in the hidden word but not in the correct position, append '+'
} else {
hint += "*"; // If the character doesn't exist in the hidden word, append '*'
}
}
return hint;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example run
HiddenWord hiddenWord = new HiddenWord("JAVA");
String guess1 = "APPLE";
String guess2 = "JUMP";
String guess3 = "JAVA";
System.out.println("Guess: " + guess1);
System.out.println("Hint: " + hiddenWord.getHint(guess1));
System.out.println("Guess: " + guess2);
System.out.println("Hint: " + hiddenWord.getHint(guess2));
System.out.println("Guess: " + guess3);
System.out.println("Hint: " + hiddenWord.getHint(guess3));
}
}
HiddenWord.main(null);
Guess: APPLE
Hint: +***
Guess: JUMP
Hint: J***
Guess: JAVA
Hint: JAVA
Explanation
It compares each character of the guess with the corresponding character in the hidden word. If a character in the guess matches the character in the same position in the hidden word, it adds that character to the hint. If a character exists in the hidden word but not in the correct position in the guess, it adds a “+” to the hint. Then, if a character doesn’t exist in the hidden word, it adds a “*” to the hint.
Reflection
This FRQ is about looking at words and the letters in them, and then seeing how those letters match up with letters in another word. It also checks if you can create and use classes in your code and pass them to functions.I just have to use .substring and if-else statements to figure out if a letter at a certain spot is in the puzzle word.
Extra
create an ArrayUtill class with the following two static properties. Complete the ArrayUtill class by writing concat() and print(), referring to the execution results of the following code.
class ArrayUtill{
public static int[] concat(int[] a, int[] b) {
int size = a.length + b.length;
int concat[] = new int[size];
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
concat[i] = a[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
concat[i + a.length] = b[i];
}
return concat;
}
public static void print(int[] a) {
System.out.print("[ ");
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
}
public class StaticEx{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array1 = {1, 5, 7, 9};
int[] array2 = {3, 6, -1, 100, 77};
int[] array3 = ArrayUtill.concat(array1, array2);
ArrayUtill.print(array3);
}
}
StaticEx.main(null);
[ 1 5 7 9 3 6 -1 100 77 ]