Directions: SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. REMEMBER THAT PROGRAM SEGMENTS ARE TO BE WRITTEN IN JAVA.
Notes:
Assume that the classes listed in the Java Quick Reference have been imported where appropriate.
Unless otherwise noted in the question, assume that parameters in method calls are not null and that methods are called only when their preconditions are satisfied.
In writing solutions for each question, you may use any of the accessible methods that are listed in classes defined in that question. Writing significant amounts of code that can be replaced by a call to one of these methods will not receive full credit.
This question involves the design of an interface, writing a class that implements the interface, and writing a method that uses the interface.
(a) A number group represents a group of integers defined in some way. It could be empty, or it could contain one or more integers.
Write an interface named NumberGroup that represents a group of integers. The interface should have a single contains method that determines if a given integer is in the group. For example, if group1 is of type NumberGroup, and it contains only the two numbers -5 and 3, then group1.contains(-5) would return true, and group1.contains(2) would return false. Write the complete NumberGroup interface. It must have exactly one method.
public interface NumberGroup {
public boolean contains(int num); // single method
}
(b) A range represents a number group that contains all (and only) the integers between a minimum value and a maximum value, inclusive. Write the Range class, which is a NumberGroup. The Range class represents the group of int values that range from a given minimum value up through a given maximum value, inclusive. For example,the declaration
NumberGroup range1 = new Range(-3, 2);
represents the group of integer values -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2.
Write the complete Range class. Include all necessary instance variables and methods as well as a constructor that takes two int parameters. The first parameter represents the minimum value, and the second parameter represents the maximum value of the range. You may assume that the minimum is less than or equal to the maximum.
public class Range implements NumberGroup {
private int min;
private int max;
public Range(int min, int max) {
this.min = min;
this.max = max;
}
@Override // overriding the method with a new one
public boolean contains(int num) {
return (num >= min && num <= max); // only returns true if num is greater than min or less than max (within range)
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Range range = new Range(-3, 2);
System.out.println("Testing 1: " + range.contains(1));
System.out.println("Testing 10: " + range.contains(10));
}
}
Range.main(null);
Testing 1: true
Testing 10: false
(c) The MultipleGroups class (not shown) represents a collection of NumberGroup objects and isa NumberGroup. The MultipleGroups class stores the number groups in the instance variable groupList (shown below), which is initialized in the constructor.
private List
Write the MultipleGroups method contains. The method takes an integer and returns true if and only if the integer is contained in one or more of the number groups in groupList.
For example, suppose multiple1 has been declared as an instance of MultipleGroups and consists of the three ranges created by the calls new Range(5, 8), new Range(10, 12), and new Range(1, 6). The following table shows the results of several calls to contains.

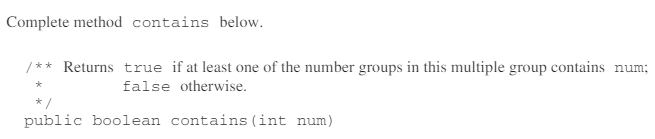
public class MultipleGroups implements NumberGroup {
private List<NumberGroup> groupList;
public MultipleGroups(List<NumberGroup> groupList) {
this.groupList = groupList;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int num) { // new method to new
for (int i = 0; i < this.groupList.size(); i++) { // looks through each of the group lists
if (this.groupList.get(i).contains(num)) { // if the number happens to be in one of the group lists, true is returned
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating multiple groups
Range r1 = new Range(5, 8);
Range r2 = new Range(10, 12);
Range r3 = new Range(1, 6);
// adding all the groups to a group list
ArrayList<NumberGroup> groupList = new ArrayList<>();
groupList.add(r1);
groupList.add(r2);
groupList.add(r3);
// creating a new instance of the group list
MultipleGroups multiple1 = new MultipleGroups(groupList);
// checking different cases to see if they are within the ranges provided
System.out.println("Testing 2: " + multiple1.contains(2));
System.out.println("Testing 9: " + multiple1.contains(9));
System.out.println("Testing 6: " + multiple1.contains(6));
}
}
MultipleGroups.main(null);
Testing 2: true
Testing 9: false
Testing 6: true